We've written extensively on the topic of email security solutions that first allow malicious emails to reach the inbox before removing them.
Our analysis found that API-based solutions take, on average, three minutes and three seconds to remediate and remove a malicious email from the inbox. Users, however, are clicking on malicious emails in an average of one minute and 22 seconds. The math is not in the user's favor.
New research, however, shows how the problem can be even worse. According to a new study, enterprise organizations take, on average, more than three days to discover and remove phishing emails that got through to the end-user. Many of these emails were found by the IT team doing internal threat hunting.
The research found that 3% of employees who receive a phishing email click on it. It takes an average of 16 minutes for the user to click, according to the study.
Whether it takes 82 seconds or 16 minutes to click, one day or three days, keeping a malicious email in the inbox for any amount of time is untenable. It takes just one click on a phishing email to cause widespread damage.
We call it the difference between Protection and Response.
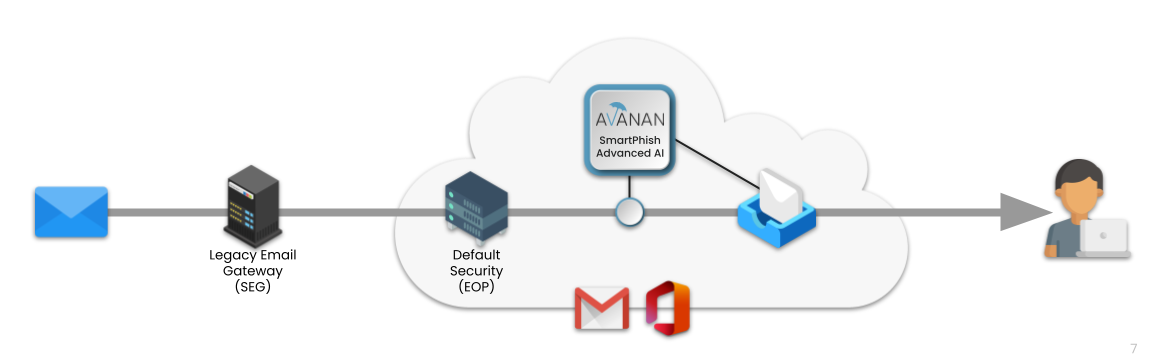
Avanan offers Protection: preventing malicious emails from reaching the end-users.
Other vendors offer Response: removing the email after it has already been delivered, typically after 30 seconds or more.
Any response time greater than zero is too long. A manual response is too late.
Avanan does things differently, by blocking malicious emails before they reach the inbox:
Here's the cost of phishing emails remaining in the inbox:
- More potential damage to the organization
- More time spent by the SOC
There's a better way. Avanan's patented solution reduces the number of emails reaching the inbox by 99.2%, and reduces the number of end-user requests to the SOC by 71.2%.
Cybersecurity moves at lightning speed—not at a leisurely pace. Leaving malicious emails in for days is a lackadaisical approach to cybersecurity.
Preventing emails from reaching the inbox is how you do cybersecurity in the modern age.







